用Python API啟動Lumerical的仿真軟件時�,建立了兩者環(huán)境之間的聯(lián)系�����,彼此的工作空間不共享�����,而是在變量傳遞過程中創(chuàng)建一個相同的副本�����,根據(jù)getv( )和put( )函數(shù)中定義的轉換類型來進行前傳和后傳。2020a R4版本將典型傳輸速率提高至約為300MBs�,并將傳輸數(shù)據(jù)所需的內(nèi)存開銷減少[1],提高了數(shù)據(jù)傳輸?shù)男?���,但當?shù)據(jù)量傳輸量非常大的時候,數(shù)據(jù)傳遞的規(guī)律仍顯得很重要。
Lumerical和Python中的數(shù)據(jù)類型對應如下:
Lumerical
| Python
|
String
| string
|
Real
| float
|
Complex
| np.array
|
Matrix
| np.array |
Cell array
| list |
Struct | dictionary
|
Dataset
| dictionary
|
仿真過程中���,經(jīng)常會從監(jiān)視器中提取各種數(shù)據(jù)類型的結果����,并進一步進行傳遞�����、數(shù)據(jù)處理��、作圖等操作���。接下來針對大家使用Python API進行仿真或提取結果時�,常涉及到的數(shù)據(jù)類型進行總結:
1. 原始數(shù)據(jù)(Raw Data)
從運行過的仿真工程中的監(jiān)視器結果中���,可以直接訪問原始數(shù)據(jù)����,這些數(shù)據(jù)在 Lumerical中以矩陣的形式存在����,將其傳遞到Python環(huán)境時���,將作為numpy數(shù)組返回。矩陣各維度的長度將與相關參數(shù)的長度一致��,與監(jiān)視器在各個維度上的監(jiān)測點個數(shù)有關�。
屬性:數(shù)據(jù)集中實際數(shù)據(jù),例如����,電場分量Ex、Ey�����、Ez是場分布監(jiān)視器的屬性����。
參數(shù):數(shù)據(jù)集的相關位置向量。例如�����,位置x��、y��、z和頻率f可以是場剖面監(jiān)視器的參數(shù)�。
用getdata( )函數(shù)可以獲取監(jiān)視器的原始數(shù)據(jù),注意與getresult( )區(qū)分�,得到數(shù)據(jù)后可以用Python的squeeze( )函數(shù),或者Lumerical的pinch( )函數(shù)來刪除單個元素的維度�,調(diào)整結果矩陣的形式。
以下是一個簡單的Python API控制Lumerical FDTD進行仿真���,并提取數(shù)據(jù)回到Python的例子:
with lumapi.FDTD() as fdtd: fdtd.addfdtd(dimension='2D', x=0.0e-9, y=0.0e-9, x_span=3.0e-6, y_span=1.0e-6) fdtd.addgaussian(name = 'source', x=0., y=-0.4e-6, injection_axis='y', waist_radius_w0=0.2e-6, wavelength_start=0.5e-6, wavelength_stop=0.6e-6) fdtd.addring( x=0.0e-9, y=0.0e-9, z=0.0e-9, inner_radius=0.1e-6, outer_radius=0.2e-6, index=2.0) fdtd.addmesh(dx=10.0e-9, dy=10.0e-9, x=0., y=0., x_span=0.4e-6, y_span=0.4e-6) fdtd.addtime(name='time', x=0.0e-9, y=0.0e-9) fdtd.addprofile(name='profile', x=0., x_span=3.0e-6, y=0.)
# Dict ordering is not guaranteed, so if there properties dependant on other properties an ordered dict is necessary# In this case 'override global monitor settings' must be true before 'frequency points' can be set props = OrderedDict([('name', 'power'), ('override global monitor settings', True), ('x', 0.),('y', 0.4e-6),('monitor type', 'linear x'), ('frequency points', 10.0)])
fdtd.addpower(properties=props) fdtd.save('fdtd_file.fsp') fdtd.run()
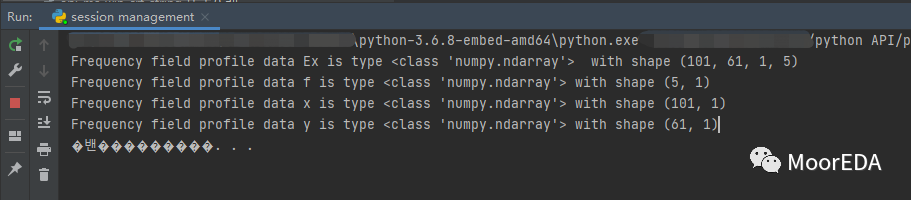
#Return raw E field data Ex = fdtd.getdata('profile','Ex') f = fdtd.getdata('profile','f') x = fdtd.getdata('profile','x') y = fdtd.getdata('profile','y')
print('Frequency field profile data Ex is type', type(Ex),' with shape', str(Ex.shape ))print('Frequency field profile data f is type', type(f), 'with shape', str(f.shape ))print('Frequency field profile data x is type', type(x), 'with shape', str(x.shape ))print('Frequency field profile data y is type', type(y), 'with shape', str(y.shape ))
Python程序設置了光源�、環(huán)形結構����、網(wǎng)格、監(jiān)視器等�,結尾處返回相應結果的維度,如下圖所示��,可以直接用Python對數(shù)據(jù)進行進一步處理���、出圖���。
2. 數(shù)據(jù)集(Datasets)
數(shù)據(jù)集是互相相關的結果,打包在Lumerical中�,可以輕松地可視化或訪問�,主要包含三種直線數(shù)據(jù)集:
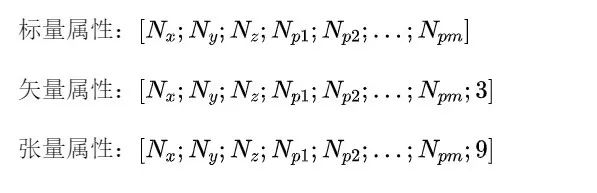
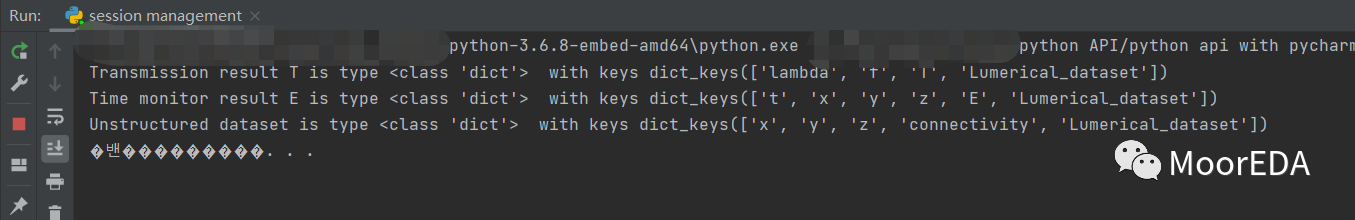
with lumapi.FDTD('fdtd_file.fsp') as fdtd: #返回兩種維度不同的數(shù)據(jù)集 T, time = fdtd.getresult('power', 'T'), fdtd.getresult('time','E')#創(chuàng)建一個非結構化數(shù)據(jù)集 fdtd.eval('x = [0;1;2];y = [0;sqrt(3);0];z = [0;0;0];C = [1,3,2];ds = unstructureddataset(x,y,z,C);') ds = fdtd.getv('ds')
print('Transmission result T is type', type(T),' with keys', str(T.keys()) )print('Time monitor result E is type', type(time),' with keys', str(time.keys()) )print('Unstructured dataset is type', type(ds),' with keys', str(ds.keys()) )
[1]https://optics.ansys.com/hc/en-us/articles/360041401434-Passing-Data-Python-API
電話:15521163312(微信同號)
郵箱:wenye@mooreda.com.cn